
Waterfall – a sequential project management approach that seeks to capture detailed requirements upfront the opposite to agile. Velocity – a measure of work completed during a single development phase or Sprint. Sprint retrospective – a review of a Sprint providing lessons learned with the aim of promoting continuous improvement. Sprints – a short development phase within a larger project defined by available time (‘timeboxes’) and resources. Scrum master – the person who oversees the development process and who makes sure everyone adheres to an agreed way of working. Scrum of scrums – a technique to operate Scrum at scale, for multiple teams working on the same product. #Agile methodology steps software
Scrum – agile methodology commonly used in software development, where regular team meetings review progress of a single development phase (or Sprint). Scaled agile – agile scaled up to large projects or programmes, for example by having multiple sub-projects, creating tranches of projects, etc. SAFe (scaled agile framework enterprise) – agile methodology used for software development. Requirements – are written as ‘stories’ that are collated into a prioritised list called the ‘Backlog’. RAD (rapid application development) – agile development method enables developers to build solutions quickly by talking directly to end users to meet business requirement. LeSS (large-scale Scrum) – agile development method. Lean – a method of working focused on ‘eliminating waste’ by avoiding anything that does not produce value for the customer. Kanban board – a work and workflow visualisation tool which summarises the status, progress, and issues related to the work. Kanban – a method for managing work, with an emphasis on just-in-time delivery. DSDM (dynamic systems development method) – agile development methodology, now changed to the ‘DSDM project management framework’. DevOps (development/operations) – bridges the gap between agile teams and operational delivery to production. 
DAD ( disciplined agile delivery) – a process-decision framework.Ceremonies – meetings, often a daily planning meeting, that identify what has been done, what is to be done and the barriers to success.Cadence – the number of days or weeks in a Sprint or release the length of the team’s development cycle.Burn down chart – used to monitor progress shows work still to complete (the Backlog) versus total time.Backlog – prioritised work still to be completed (see Requirements).Responding to change over following a plan. Customer collaboration over contract negotiation. Working software over comprehensive documentation. Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
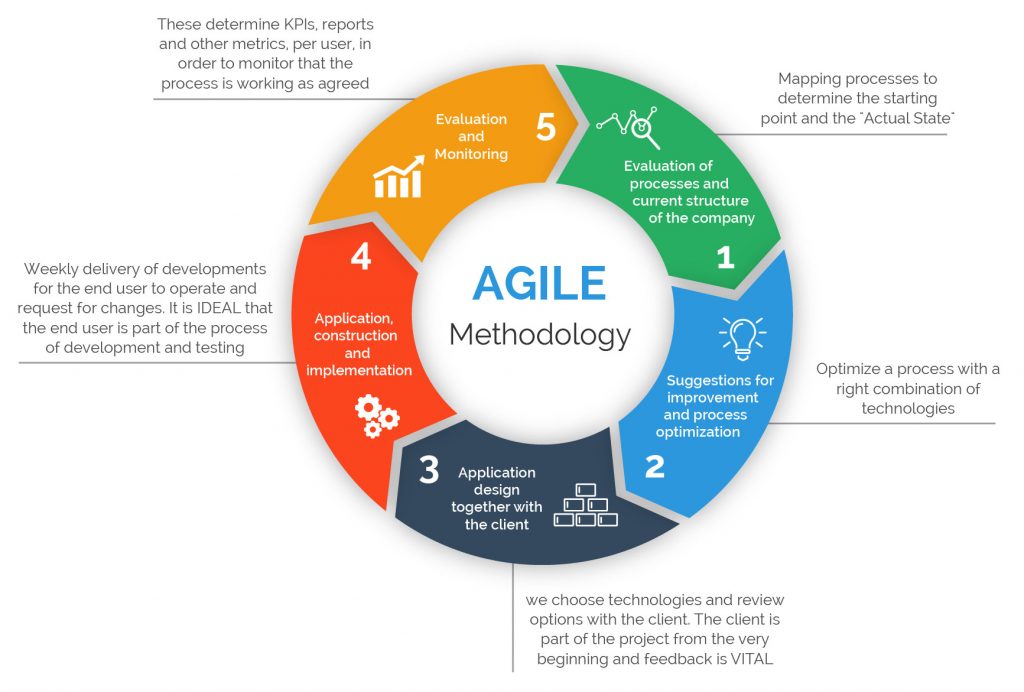
Agile Manifesto – describes the four principles of agile development: 1.
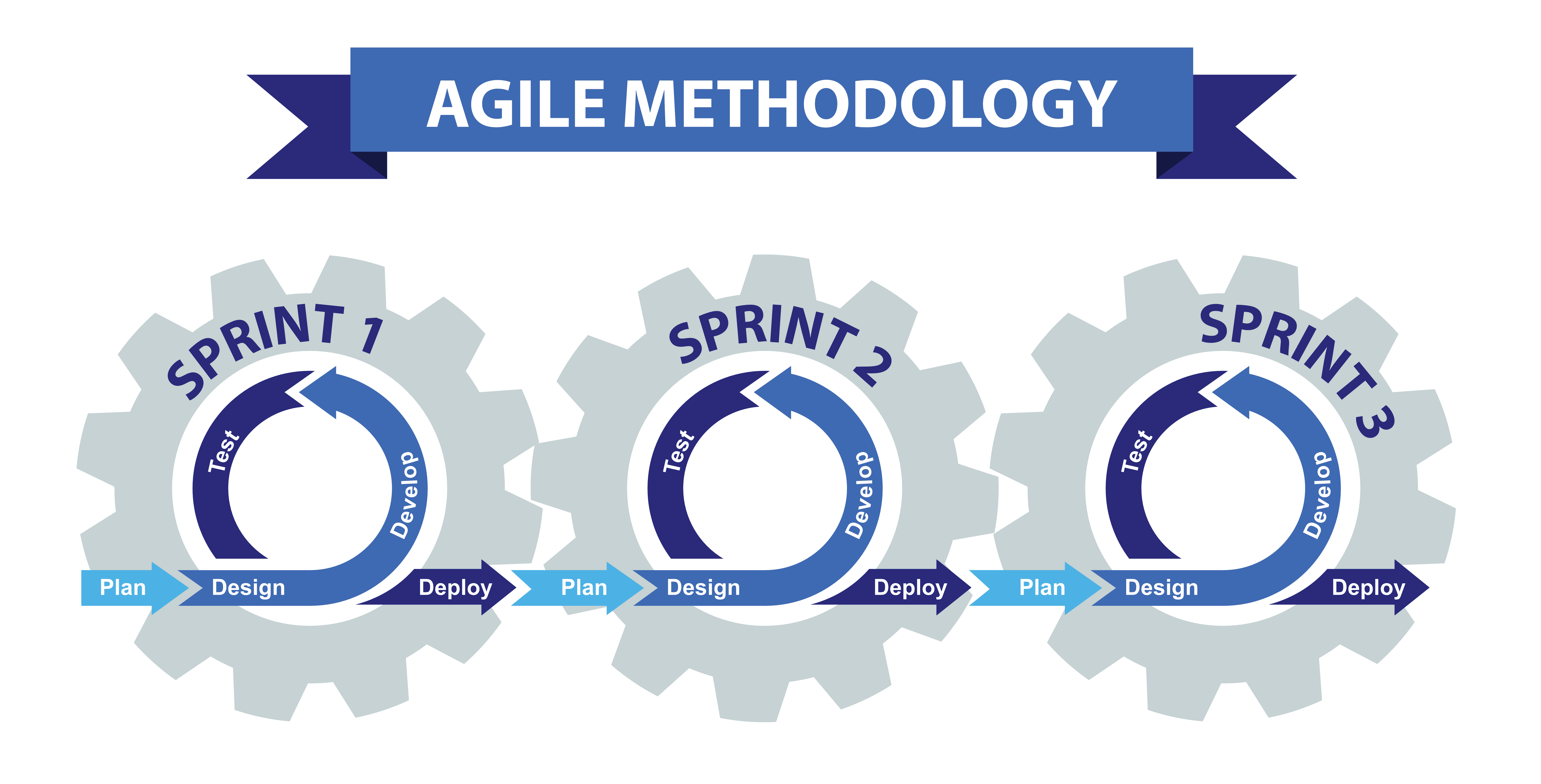
Popular methods include Scrum, Lean, DSDM and eXtreme Programming (XP). Agile development – an umbrella term specifically for iterative software development methodologies.Agile – a project management approach based on delivering requirements iteratively and incrementally throughout the life cycle.

We have compiled a list of the most common agile terminology you may come across, and their definitions: Iterative or agile terminology can be confusing.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
